
On Android devices, the equivalent of the Task Manager is called the “Recent Apps,” “Overview” screen, or the “App Switcher.” It allows you to view and manage your recently opened apps. Here’s how to access it:
For devices with a physical or on-screen navigation bar:
- Look for a square or a group of three lines (≡) on your navigation bar. This icon represents the “Recent Apps” button.
- Tap the “Recent Apps” button to see a list of your recently opened applications.
or,
- Locate the navigation buttons at the bottom of your screen. If you’re using a device with gesture navigation, swipe up from the bottom of the screen to reveal these buttons.
- Tap the square or “Recent Apps” button, usually located in the bottom right or left corner. On some devices, you might need to tap the “Overview” button, which looks like two rectangles stacked on top of each other.
- You’ll see a list of your recently used apps in a scrolling view.
- To switch between apps, tap the app you’d like to use.
- To close an app, swipe it to the left or right, or tap the “X” button if it’s available. On some devices, you might need to swipe up or down to close the app.
For devices with gesture-based navigation:
- Swipe up from the bottom of the screen and hold your finger for a moment. This will bring up the “Recent Apps” screen.
- If your device has a different gesture, consult your device’s user manual or settings for information on how to access the “Recent Apps” screen.
Once you’ve accessed the “Recent Apps” screen, you can swipe left or right to navigate through your recently opened apps, swipe up or down (depending on your device) to close an app or tap on an app to switch to it. Some devices also offer additional options for managing apps, such as locking them in the recent apps list, accessing app settings, or splitting the screen for multitasking. These options can usually be found by tapping the app icon or a menu button within the “Recent Apps” screen.
Keep in mind that the appearance and functionality of the Recent Apps screen may vary slightly between different Android devices and versions. However, the general concept of accessing and managing your running apps should be similar.
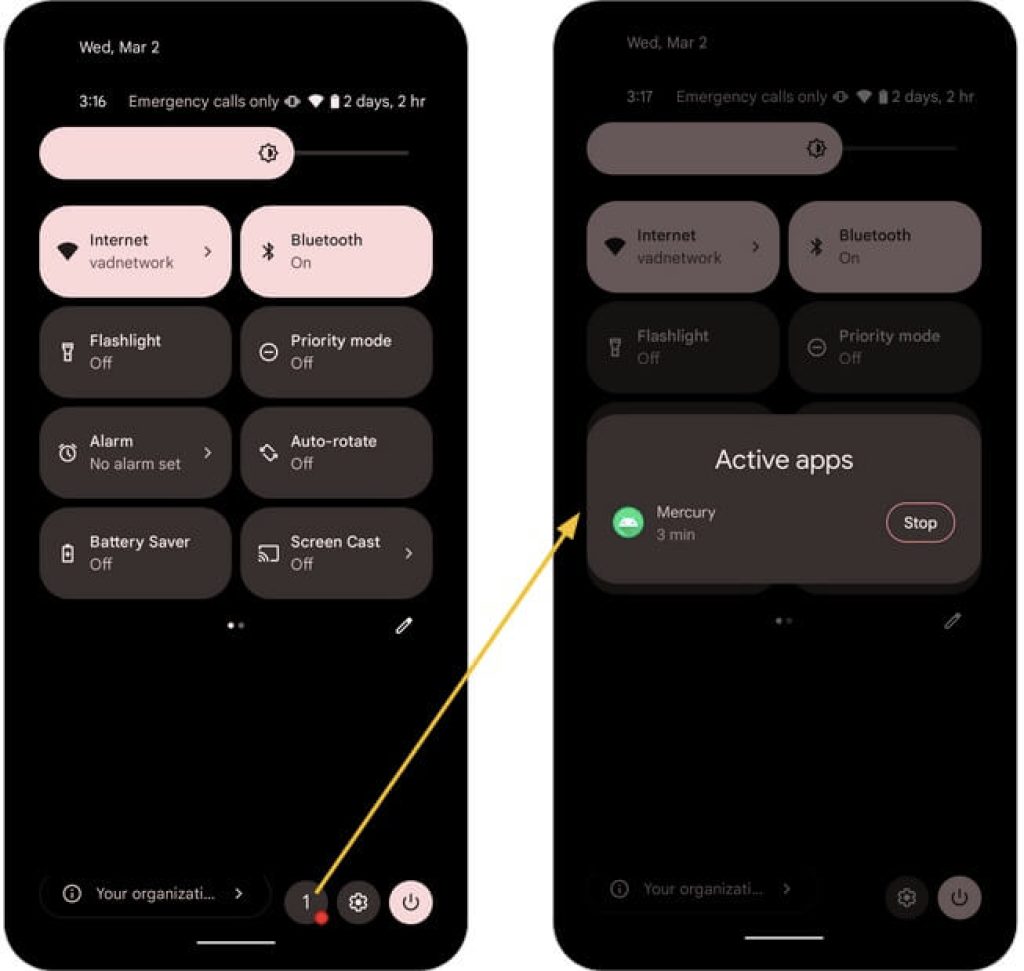
Starting with Android 13 (API level 33), users can access a workflow from the notification drawer that enables them to terminate an app with ongoing foreground services, irrespective of the app’s target SDK version. This feature, known as the Task Manager, presents a list of apps that have an active foreground service at the moment.
The list is titled Active Apps, and a Stop button is situated beside each app. Figure 1 demonstrates the Task Manager process on a device powered by Android 13.
When a user clicks the Stop button adjacent to your app in the Task Manager, the subsequent events take place:
- The system removes your app from memory, causing your entire app to cease, not just the active foreground service.
- The system clears your app’s activity back stack.
- Any media playback is halted.
- The notification linked to the foreground service is removed.
- Your app remains in history.
- Scheduled tasks are executed at their predetermined time.
- Alarms are triggered at their planned time or time frame.





